Diabetes Mellitus is one of the rapidly increasing health issues globally, and in India as well. In the year 2026, Diabetes is no longer a “sugar problem” but a lifestyle-related metabolic disorder that impacts the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and quality of life.
The good news?
Early diagnosis, proper diet, lifestyle changes, and new treatments can help control diabetes.
Table of Contents
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition where the blood glucose/sugar level is persistently high due to:
- The pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or
- The body cannot use insulin effectively (insulin resistance).
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps glucose enter cells to produce energy. Insulin doesn’t work well if sugar cannot enter cells, and this causes diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
- Typically presents in children or young adolescents.
- Autoimmune disease.
- The body ceases to produce insulin entirely.
- Requires insulin therapy throughout life.
Type 2 Diabetes (Most Common)
- Primarily found in adults, but now rising among the young.
- Due to insulin resistance and inefficient insulin secretion.
- Strongly linked with physical inactivity, poor diet, and obesity.
Gestational Diabetes
- Happens during pregnancy.
- Typically resolves after childbirth.
- Raises the risk of Type 2 diabetes in the future.
Causes & Risk Factors of Diabetes
Major Causes
- Poor diet (high sugar, refined carbohydrates).
- Lack of physical activity.
- Obesity (particularly visceral fat).
- Genetic predisposition.
- Chronic stress.
- Poor sleep patterns.
High-Risk Groups
- Family history of diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- PCOS in women.
- High blood pressure or cholesterol.
- Age above 30 years (earlier now).
Early Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
This is because many people are not diagnosed as the symptoms develop gradually.
Common Symptoms
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Poor wound healing
- Recurrent infections
Important– Type 2 diabetes can be asymptomatic for years, silently damaging organs without showing clear signs.
Diagnosis & Tests for Diabetes Mellitus
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
- Normal: < 100 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 126 mg/dL
2. Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS)
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL (2 hours after meal)
3. HbA1c (Gold Standard Test)
- Normal: < 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7–6.4%
- Diabetes: ≥ 6.5%
4. Random Blood Sugar
- ≥ 200 mg/dL with symptoms suggests diabetes
Indian Diet Chart for Diabetes
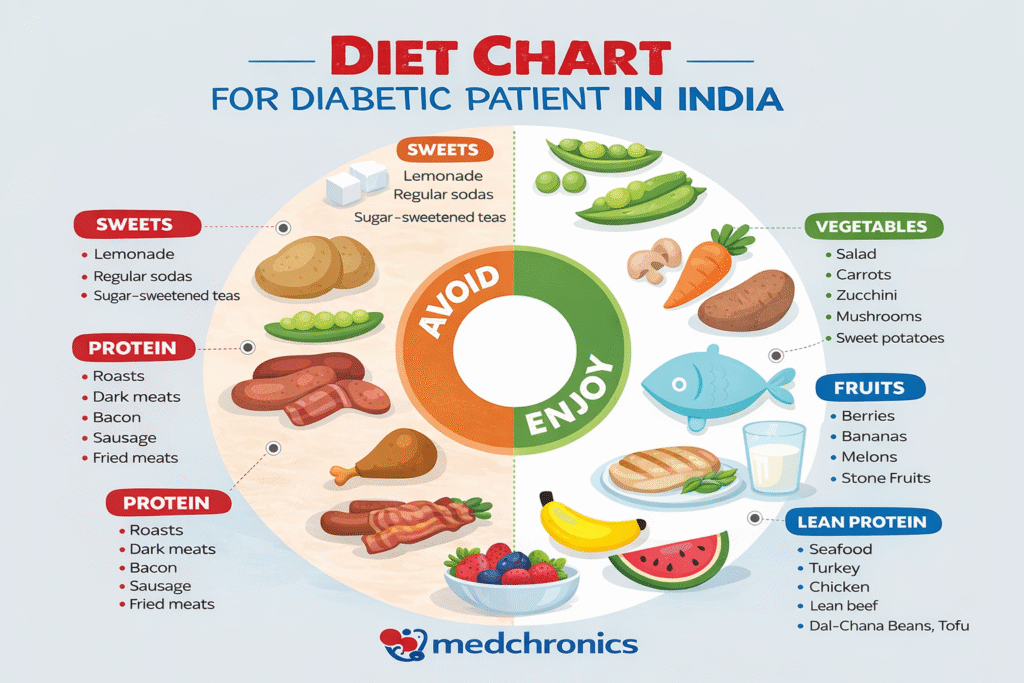
A balanced diet is often considered the best medicine for controlling diabetes.
Foods to Eat (Low Glycemic Index)
Breakfast
- Vegetable poha.
- Oats with nuts.
- Besan chilla.
- Boiled eggs/paneer.
Lunch
- Multigrain roti / brown rice.
- Dal/rajma/chole.
- Green vegetables (lauki, bhindi, tori).
- Curd (unsweetened).
Evening Snack
- Roasted chana.
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts).
- Sprouts.
Dinner (Light)
- Vegetable soup.
- Roti + sabzi.
- Grilled paneer/fish.
Foods to Avoid
- Sugar, sweets, bakery products.
- White rice, maida, noodles.
- Sugary drinks and packaged juices.
- Fried and processed foods.
Lifestyle Modifications for Controlling Diabetes
1. Physical Activity
- 30–45 minutes of brisk walking every day.
- Strength training 2–3 times a week.
- Yoga and pranayama practices help reduce stress.
2. Weight Management
- Losing 5–7% of body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
3. Sleep & Stress Control
- Aim for 7–8 hours of good-quality sleep.
- Practice meditation and breathing exercises regularly.
4. Quit Smoking & Limit Alcohol
- Smoking increases insulin resistance.
- Alcohol can cause blood sugar fluctuations.
Latest Treatment Options for Diabetes
1. Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs
- Metformin (first-line therapy)
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (protective for the heart and kidneys)
2. Injectable Therapies
- GLP-1 receptor agonists (help with weight loss)
- Long-acting insulin analogues
3. Personalized Treatment Approach
- Tailored according to age, weight, and heart/kidney health
- Focuses on cardio-renal protection
4. Technology-Based Management
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- Smart insulin pens
- Mobile health applications
Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
If diabetes is not controlled, it can cause several complications:
Short-Term
- Hypoglycaemia
- Hyperglycaemia
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Long-Term
- Heart disease & stroke
- Kidney failure
- Diabetic retinopathy (vision loss)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Diabetic foot ulcers
Regular monitoring can prevent most complications.
Can Diabetes Be Reversed?
- Type 1 Diabetes: Not reversible
- Type 2 Diabetes: Can be managed and sometimes reversed in the early stages
- Prediabetes: Highly reversible with lifestyle changes
Early action is the key.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is diabetes permanently curable?
There’s no permanent cure, but diabetes can be effectively managed for life.
Q2. Can diabetics eat rice?
Yes, but in moderation. Choose brown rice or eat small portions rich in fiber.
Q3. Is sugar the only cause of diabetes mellitus?
No. Lifestyle habits, obesity, and genetics play a much bigger role.
Q4. How often should blood sugar be checked?
For Controlled patients: every 3 months (HbA1c)
For Uncontrolled: more frequently, as advised by a doctor
Q5. Can walking alone control diabetes?
Walking helps, but maintaining a healthy diet and taking medicines are equally essential.
Q6. What does diabetes mellitus mean?
Diabetes mellitus is a long-term (chronic) medical condition in which the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood remains higher than normal.

